Understanding the Different Types of 3D Printing Materials
Introduction to 3D Printing Materials
3D printing has revolutionized the way we approach manufacturing and prototyping. One of the key aspects of this technology is the variety of materials that can be used. Each material offers unique properties and advantages, making it crucial to understand what options are available and how they might suit your specific needs.
In this blog, we'll explore the different types of 3D printing materials, providing insights into their characteristics and applications. Whether you are a hobbyist or a professional, understanding these materials can help you make informed decisions for your projects.

Thermoplastics
PLA (Polylactic Acid)
PLA is one of the most popular 3D printing materials due to its ease of use and eco-friendly nature. It's derived from renewable resources like corn starch or sugarcane. PLA is perfect for beginners, offering a smooth finish and low warping. It's ideal for creating aesthetic models and prototypes that don't require high strength.
ABS (Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene)
ABS is a strong, durable plastic that is commonly used for functional parts and prototypes. It is more heat-resistant than PLA, making it suitable for objects that need to withstand higher temperatures. However, it requires a heated bed during printing and can emit fumes, necessitating a well-ventilated environment.

Resins
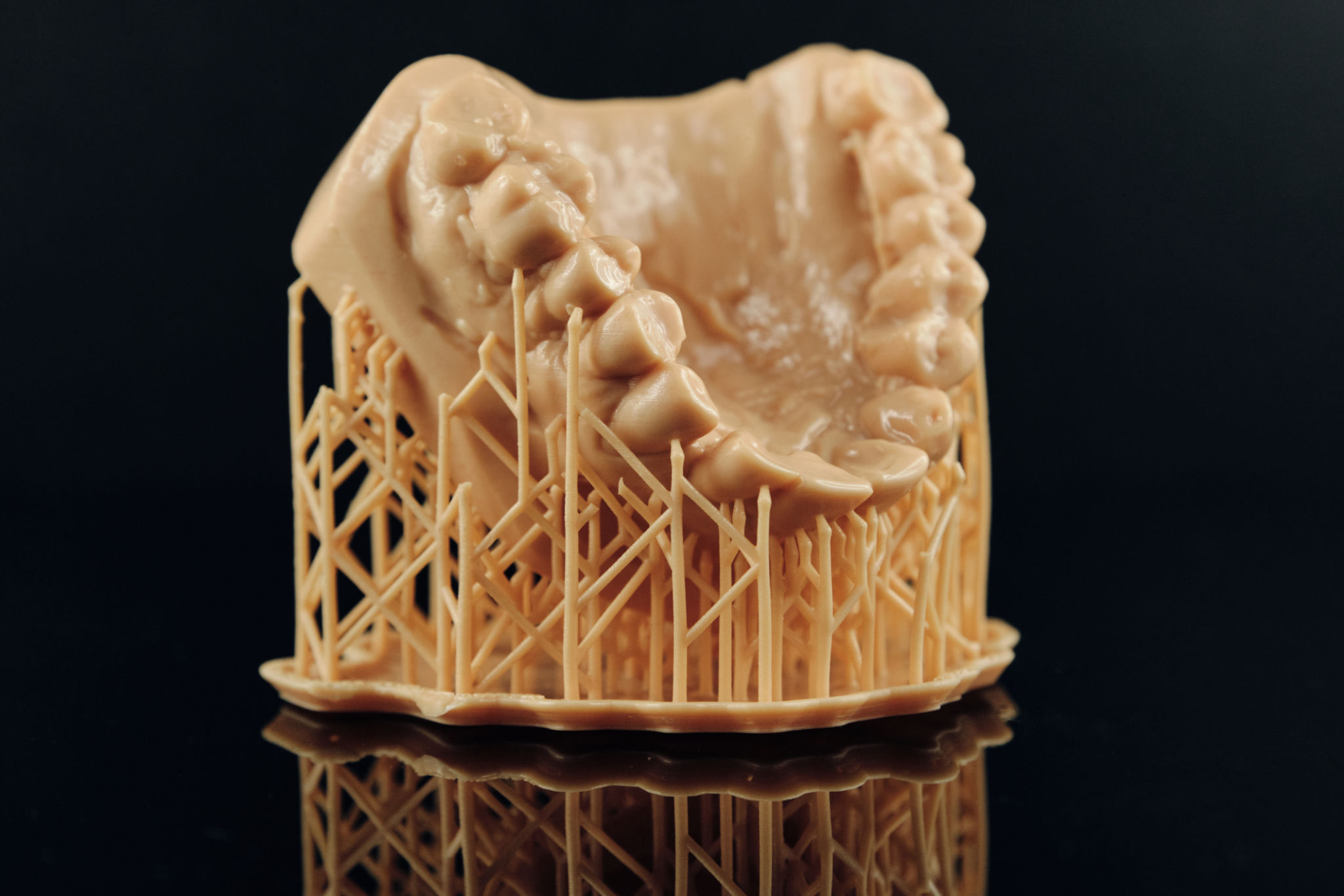
SLA Resin
Stereolithography (SLA) resins are known for producing highly detailed prints. These resins cure under UV light, providing smooth surfaces and intricate details. They are perfect for applications in jewelry, dental models, and other fields where precision is paramount. However, prints require post-curing to achieve optimal strength.
Flexible Resin
Flexible resins offer elasticity and can be used to create rubber-like parts. This material is ideal for prototypes that need to bend or compress without breaking. It's commonly used in fashion design, medical models, and other applications where flexibility is crucial.
Metals
Stainless Steel
Metal 3D printing has expanded the possibilities for creating robust and long-lasting parts. Stainless steel is widely used for its strength and resistance to corrosion. It's often utilized in industries like aerospace, automotive, and healthcare to produce complex geometries that traditional manufacturing cannot achieve.
Titanium
Titanium is known for its high strength-to-weight ratio and biocompatibility. This makes it an excellent choice for medical implants and aerospace components. Although more expensive than other materials, its unique properties justify its use in critical applications where performance cannot be compromised.

Composites
Carbon Fiber
Carbon fiber composites are becoming increasingly popular in 3D printing for their excellent strength-to-weight ratio. These materials are used in demanding industries such as automotive and sports equipment manufacturing. They provide enhanced mechanical properties without significantly increasing weight.
Wood Filaments
Wood filaments combine PLA with wood fibers, offering a unique aesthetic appeal with a natural wood look and feel. They are perfect for artistic projects and decorative items. The printed objects can also be sanded and stained, similar to real wood, adding versatility to your creations.
The world of 3D printing materials is vast and constantly evolving. By understanding the different types of materials available, you can harness the full potential of 3D printing technology. Whether you're focused on aesthetics, functionality, or durability, there's a material out there that fits your needs.
